
API First Design in FastAPI
Pattens and tips for writing better code
Overwriview
- 🛠 What is API First Deign
- 📝 How to do it
- 🎨 Examples
Overwriview
- 🛠 What is API First Deign
- 📝 How to do it
- 🎨 Examples
The last comment block of each slide will be treated as slide notes. It will be visible and editable in Presenter Mode along with the slide. Read more in the docs
API First Design in FastAPI
Pattens and tips for writing better code
Overwriview
- 🛠 What is API First Deign
- 📝 How to do it
- 🎨 Examples
What is API First Design
An API design-first approach is about describing every API design in an iterative way that both humans and computers can understand—before you write any code. Where API-first is about putting APIs front and center, API design-first is about the process of creating the API itself.

What is API First Design
An API design-first approach is about describing every API design in an iterative way that both humans and computers can understand—before you write any code. Where API-first is about putting APIs front and center, API design-first is about the process of creating the API itself.

What is API First Design
There are three principles of API First Design:
Your API is the first user interface of your application
Your API comes first, then the implementation
Your API is described (and maybe even self-descriptive)
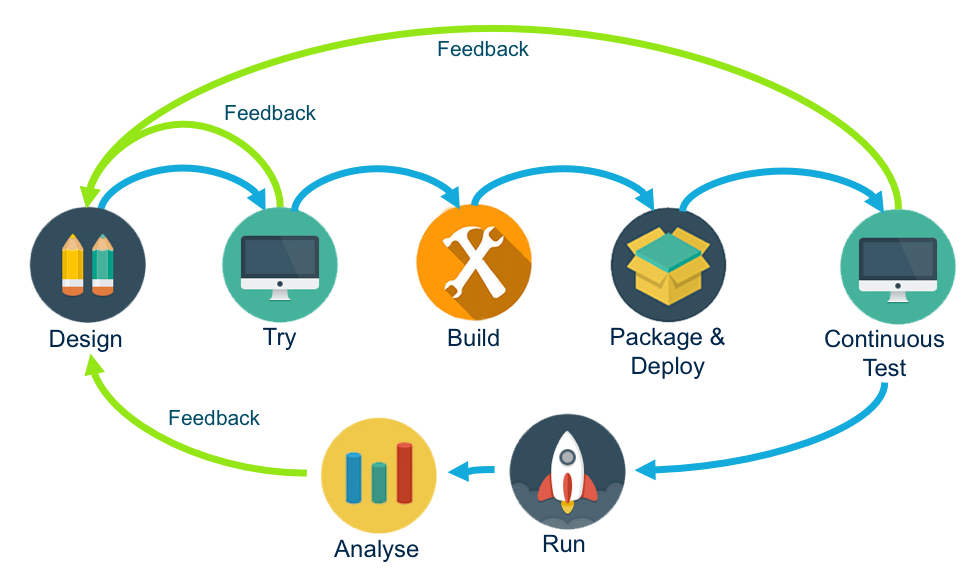
How to do it
Here are the steps:
- Defining the API type
- Single-Purpose APIs: These are APIs that serve a unique and specific purpose, typically derived from an unambiguous need associated with a user journey or use case.
- Multi-Purpose APIs: These APIs are more generic in nature and are meant to satisfy not just one but multiple use cases and scenarios.
- Creating the API definition with its main resources: This step shows how to create an API and define its main resources, parameters, and sample payloads.
- Trying the API mock: This part describes how Apiary’s automatically generated API mocks can be used to satisfy one of the most important steps in API design-first: try an API early in the lifecycle, before the API is actually implemented.
- Pushing the API : Push it to a site so others can start to play with it and give feedback
How to do it in code level
- Design your tables and model if needed
- Define request and response model in
schemas.py - Deinde API
endpointandmethodinrouter.py - Write request and response sample
Example Case for Countrypedia
We’ll build an apis here and skip the database design part, GET /countrypedia/countries: Returns list of countries supported by CountryPedia For each countries
- create data model in
schema.py, and write some sample response - create router group and define the endpoint in
router.py - check Swagger online
Example Case for Countrypedia
create single data model in schema.py, and write some sample response
class CountryResponse(BaseModel): alpha_code: str = Field(name="alpha_code",description="The alpha_code code for the country",max_length=300) name: str = Field(title="name",description="The English name for the country") name_cn: str = Field(title="name_cn", description="The Chinese name for the country") flag: str = Field(title="flag", description="The flag for the country") class Config: schema_extra = { "example": { "alpha_code": "ALA", "name": "Aland lslands", "name_cn": "奥兰群岛", "flag": "", } }class CountryResponse(BaseModel): alpha_code: str = Field(name="alpha_code",description="The alpha_code code for the country",max_length=300) name: str = Field(title="name",description="The English name for the country") name_cn: str = Field(title="name_cn", description="The Chinese name for the country") flag: str = Field(title="flag", description="The flag for the country") class Config: schema_extra = { "example": { "alpha_code": "ALA", "name": "Aland lslands", "name_cn": "奥兰群岛", "flag": "", } }
Example Case for Countrypedia
create list data model in schema.py, and write some sample response
class CountriesResponse(BaseModel): __root__: list[CountryResponse] class Config: schema_extra = { "example": { "total": 2, "page_number": 0, "page_size": 10, "rows": [ { "alpha_code": "ALA", "name": "Aland lslands", "name_cn": "奥兰群岛", "flag": "", }, { "alpha_code": "ATG", "name": "Antigua and Barbuda", "name_cn": "安提瓜与巴布达", "flag": "", }, ], } }class CountriesResponse(BaseModel): __root__: list[CountryResponse] class Config: schema_extra = { "example": { "total": 2, "page_number": 0, "page_size": 10, "rows": [ { "alpha_code": "ALA", "name": "Aland lslands", "name_cn": "奥兰群岛", "flag": "", }, { "alpha_code": "ATG", "name": "Antigua and Barbuda", "name_cn": "安提瓜与巴布达", "flag": "", }, ], } }
Example Case for Countrypedia
create endpoint in the router
router = APIRouter( prefix="/countrypedia", tags=["countrypedia"], ) @router.get( "/countries", summary="Returns list of countries supported by CountryPedia", description=""" Returns list of countries supported by CountryPedia For each countries: Fields: alpha code, name, name_cn,flag, list of supported regions (others tbd) """, response_model=Response[PaginationData[CountriesResponse]], ) async def get_countries(user_id: int = Depends(get_user_id)): passrouter = APIRouter( prefix="/countrypedia", tags=["countrypedia"], ) @router.get( "/countries", summary="Returns list of countries supported by CountryPedia", description=""" Returns list of countries supported by CountryPedia For each countries: Fields: alpha code, name, name_cn,flag, list of supported regions (others tbd) """, response_model=Response[PaginationData[CountriesResponse]], ) async def get_countries(user_id: int = Depends(get_user_id)): pass
Try it by yourself
- code can be found at https://gitlab.com/rocketg/service/sample/-/tree/countrypedia

Thank You!
